Understanding Human Metapneumovirus: Symptoms, Transmission, and Prevention
We will explore an important respiratory virus called Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV). Understanding this virus is crucial for safeguarding our health and taking appropriate measures to prevent its spread.
We will explore an important respiratory virus called Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV). Understanding this virus is crucial for safeguarding our health and taking appropriate measures to prevent its spread. Join us as we delve into the details of HMPV, including its symptoms, transmission, and prevention strategies.
What is Human Metapneumovirus?
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) can cause upper and lower respiratory disease in people of all ages, especially among young children, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems. It was identified in 2001 by scientists in the Netherlands. HMPV is in the Pneumoviridae family along with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Broader use of molecular diagnostic testing has increased identification and awareness of HMPV as an important cause of upper and lower respiratory infection.
Who might get human metapneumovirus?
- Children under 5
- People over 65
- People with asthma who use steroids.
- People with COPD
- Newborns
- People who are immunocompromised, such as those who take cancer medications or have had organ transplants
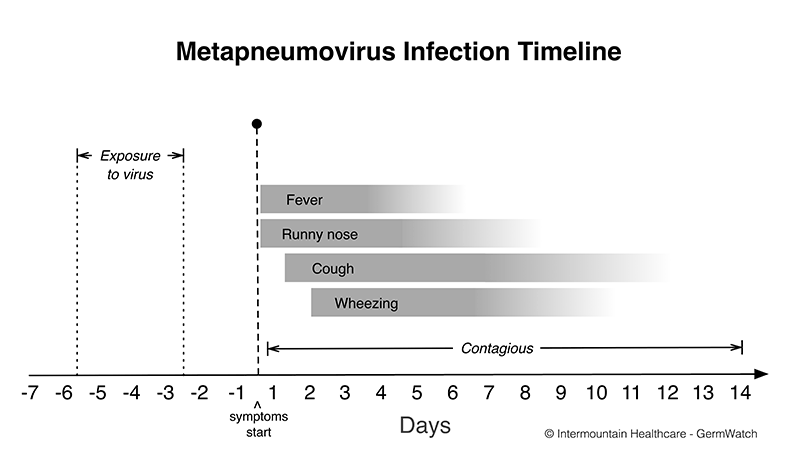
How It's Spread
- secretions from coughing and sneezing
- close personal contact, such as touching or shaking hands
- touching objects or surfaces that have the viruses on them then touching the mouth, nose, or eyes
Symptoms of HMPV
People with hMPV typically experience mild symptoms similar to a cold, according to the American Lung Association. Symptoms last about two to five days and usually resolve on their own in healthy individuals.
The common symptoms include:
- Cough
- Fever
- Nasal congestion
- Shortness of breath
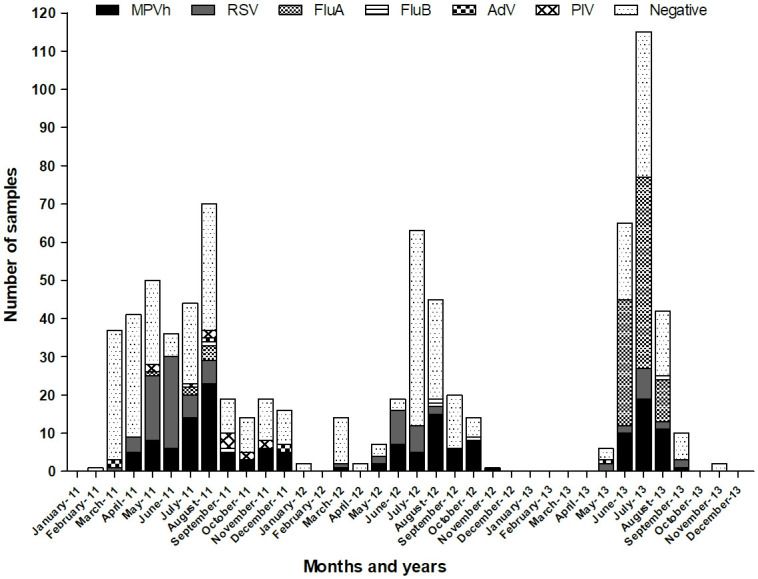
Prevention of HMPV
- Wash their hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds
- Avoid touching their eyes, nose, or mouth with unwashed hands
- Avoid close contact with people who are sick
- avoid sharing cups and eating utensils with others
- refrain from kissing others
- stay at home when they are sick
Conclusion:
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a respiratory virus that can cause a range of symptoms, from mild cold-like symptoms to severe respiratory conditions. By understanding the symptoms, modes of transmission, and prevention strategies associated with HMPV, we can take proactive measures to protect ourselves and those around us. Remember, practicing good hand hygiene, maintaining respiratory etiquette, and staying home when sick are crucial steps in preventing the spread of HMPV and other respiratory infections. Stay safe and keep your respiratory health.




