Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Revolutionizing Business Operations
In today's fast-paced digital world, businesses are constantly seeking innovative solutions to streamline their operations and enhance productivity. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has emerged as a game-changing technology that automates repetitive and mundane tasks, freeing up human resources

Introduction to Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
In today's fast-paced digital world, businesses are constantly seeking innovative solutions to streamline their operations and enhance productivity. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has emerged as a game-changing technology that automates repetitive and mundane tasks, freeing up human resources to focus on more strategic and value-added activities. This article explores the concept of RPA, its benefits, implementation challenges, and its impact on various industries.
Understanding Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) refers to the use of software robots or "bots" to perform rule-based tasks and processes, mimicking human actions within digital systems. These bots are trained to interact with applications, manipulate data, trigger responses, and execute routine tasks, essentially emulating human actions in a structured and rule-driven environment.
RPA can be applied to a wide range of activities, including data entry, data manipulation, transaction processing, report generation, data validation, and more. It integrates seamlessly with existing systems, requiring minimal disruption to the underlying infrastructure.
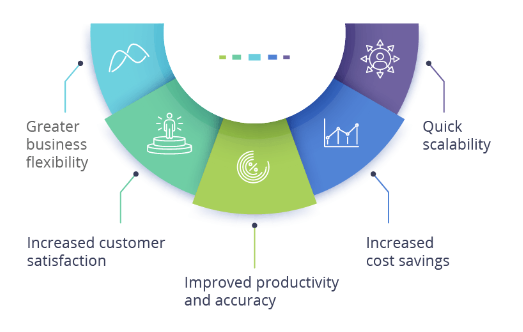
Benefits of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Increased Efficiency:
RPA eliminates manual errors, accelerates task execution, and improves process efficiency. Bots work tirelessly, 24/7, without the need for breaks or vacations, ensuring uninterrupted productivity.
Cost Savings:
By automating repetitive tasks, organizations can significantly reduce labor costs, reallocating resources to higher-value activities. RPA also eliminates the need for additional hardware or software investments, making it a cost-effective solution.
Improved Accuracy:
RPA bots perform tasks with high precision and accuracy, minimizing the risk of human error. This leads to improved data quality and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
Enhanced Scalability:
RPA allows businesses to scale operations rapidly without incurring additional overheads. Bots can handle increased workloads effortlessly, adapting to changing business demands.
Employee Empowerment:
RPA frees up employees from mundane and repetitive tasks, enabling them to focus on creative and strategic endeavors. This enhances job satisfaction and promotes employee engagement.
Implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
While the benefits of RPA are enticing, its successful implementation requires careful planning and execution. Here are the key steps involved in implementing RPA:
Process Analysis:
Identify processes suitable for automation. Analyze tasks, workflows, and dependencies to determine the potential benefits and feasibility of RPA implementation.
Vendor Selection:
Choose a reliable RPA vendor that aligns with your business requirements. Consider factors such as scalability, security, flexibility, and support when selecting an RPA solution provider.
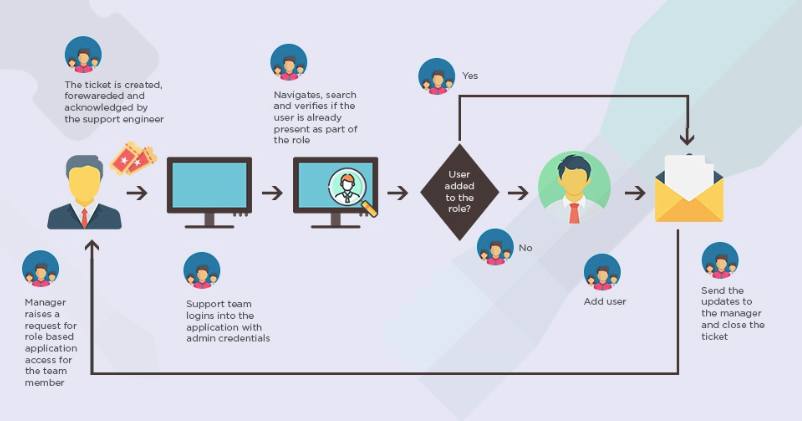
Design and Development:
Work closely with the RPA vendor to design and develop automation workflows. Define rules, triggers, and exception-handling mechanisms to ensure smooth execution.
Testing and Deployment:
Thoroughly test the automation workflows in a controlled environment to identify and rectify any issues. Once validated, deploy the bots into the production environment.
Monitoring and Maintenance:
Regularly monitor the performance of RPA bots and make necessary adjustments as business needs evolve. Provide ongoing maintenance and support to ensure smooth operation.
Challenges and Limitations of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)

While RPA offers numerous benefits, there are certain challenges and limitations that organizations need to consider:
Process Complexity:
RPA is most effective when applied to rule-based, repetitive tasks. Processes involving complex decision-making, unstructured data, or subjective judgments may require human intervention.
Data Security and Compliance:
As RPA deals with sensitive data and interacts with various systems, making data security and compliance crucial considerations. Organizations must ensure that the RPA implementation complies with industry regulations and data protection standards.
Resistance to Change:
Introducing automation through RPA may face resistance from employees who fear job displacement. It is important to communicate the benefits of RPA and provide proper training to employees to alleviate concerns and facilitate a smooth transition.
Process Standardization:
RPA relies on standardized processes and structured data. In cases where processes are not well-documented or lack standardization, additional efforts may be required to streamline and optimize processes before implementing RPA.
Integration Challenges:
Integrating RPA with legacy systems or complex IT environments can pose technical challenges. It is essential to assess the compatibility and feasibility of integrating RPA with existing systems and applications.
Maintenance and Scalability:
RPA requires ongoing maintenance to ensure its continued effectiveness. As processes change and evolve, bots may need to be updated or reconfigured. Scaling up RPA initiatives across the organization also requires careful planning and resource allocation.
RPA Applications in Various Industries
The potential applications of RPA extend across industries, revolutionizing operations and driving efficiency gains. Here are some examples of how RPA is being used:
Banking and Finance:
RPA automates data entry, loan processing, customer onboarding, account reconciliation, compliance reporting, and fraud detection. It streamlines back-office operations, reduces processing time, and improves customer service.
Healthcare:
RPA automates patient registration, claims processing, appointment scheduling, billing, and medical record management. It enhances accuracy, reduces administrative burdens, and enables healthcare professionals to focus on patient care.
Retail and E-commerce:
RPA automates inventory management, order processing, invoice generation, and customer support. It improves order accuracy, speeds up fulfillment, and enhances customer experience.
Manufacturing:
RPA automates supply chain management, inventory tracking, production reporting, and quality control. It optimizes production processes, reduces errors, and enables real-time monitoring of operations.
Human Resources:
RPA automates employee onboarding, payroll processing, benefits administration, leave management, and performance tracking. It streamlines HR processes, reduces manual errors, and enhances employee experience.
Insurance:
RPA automates policy administration, claims processing, underwriting, and risk assessment. It accelerates claims settlement, improves accuracy, and enhances customer satisfaction.
The Future of RPA
The future of RPA looks promising, with continued advancements and evolving capabilities. Here are some trends and developments to watch for:
Cognitive Automation:
RPA combined with Artificial Intelligence (AI) enables cognitive automation, allowing bots to handle complex tasks involving decision-making, natural language processing, and data analysis.
Hyperautomation:
Hyperautomation involves integrating RPA with other automation technologies, such as AI, machine learning, and process mining, to achieve end-to-end automation and further enhance efficiency and productivity.
Intelligent Process Automation (IPA):
IPA combines RPA, AI, and machine learning to automate not only repetitive tasks but also complex processes that involve unstructured data, reasoning, and problem-solving.
Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS):
RaaS models enable organizations to access RPA capabilities without significant upfront investments. This approach allows businesses to scale their automation initiatives as needed, paying for services on a subscription or usage basis.
Collaborative Automation:
Collaborative robots or "cobots" work alongside human employees, enhancing collaboration and productivity. These cobots can perform tasks that require physical interaction or decision-making based on human input, enabling human-robot collaboration in various domains.
Process Discovery and Automation:
Advances in process mining techniques allow organizations to identify and analyze existing processes to identify automation opportunities. This helps in automating processes that were previously difficult to document or standardize.
RPA Governance and Security:
As RPA adoption increases, organizations will focus on establishing robust governance frameworks and implementing stringent security measures to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with regulations.
Expanded Industry Adoption:
RPA is expected to witness widespread adoption across industries, including government, logistics, energy, and telecommunications, as organizations recognize the significant benefits of automation in improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has emerged as a transformative technology that revolutionizes business operations by automating repetitive and rule-based tasks. With its potential to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance accuracy, RPA is being widely adopted across various industries.
While there are challenges and limitations associated with RPA implementation, organizations can overcome them through careful planning, employee training, and effective change management. As RPA evolves, cognitive automation, hyper-automation, and collaborative automation will shape the future of the technology.
By leveraging RPA and embracing automation, businesses can unlock significant competitive advantages, allowing human employees to focus on higher-value activities, driving innovation, and delivering superior customer experiences. The future of RPA holds immense potential, promising to reshape the way organizations operate and thrive in the digital age.




