Exploring the Latest Tech Topics: A Comprehensive Overview
From artificial intelligence and quantum computing to augmented reality and blockchain, we will delve into these exciting areas.

Introduction
The world of technology is constantly evolving, with new advancements and innovations emerging every day. In this article, we will explore some of the latest tech topics that have been making waves in recent times. From artificial intelligence and quantum computing to augmented reality and blockchain, we will delve into these exciting areas and discuss their potential impact on various industries.
Artificial Intelligence
1. Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Machine learning and deep learning are subfields of artificial intelligence that have gained significant attention in recent years. These technologies involve training algorithms to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. They find applications in various domains, including image recognition, natural language processing, and recommendation systems. Machine learning and deep learning have the potential to revolutionize industries such as healthcare, finance, and transportation.
2. Ethical Considerations in AI
As artificial intelligence becomes more advanced and pervasive, ethical considerations become increasingly important. Issues such as bias in algorithms, job displacement, and data privacy need to be carefully addressed. The responsible development and deployment of AI systems require transparency, accountability, and inclusive decision-making processes. It is crucial to ensure that AI technologies are developed and used in a manner that benefits society as a whole.
Quantum Computing
1. Quantum Supremacy
Quantum computing has the potential to solve complex problems that are currently infeasible for classical computers. Quantum supremacy refers to the point at which a quantum computer can perform a calculation that surpasses the capabilities of the most powerful classical computers. This milestone has recently been achieved by some leading companies and research institutions. Quantum supremacy opens up possibilities for advancements in cryptography, optimization, and material science.
2. Practical Applications of Quantum Computing
While quantum computing is still in its early stages, there are several potential practical applications on the horizon. These include drug discovery, weather forecasting, optimization of complex systems, and financial modeling. Quantum computers have the ability to solve problems exponentially faster than classical computers, which could lead to breakthroughs in various fields.
Take a look at:

Augmented Reality (AR)
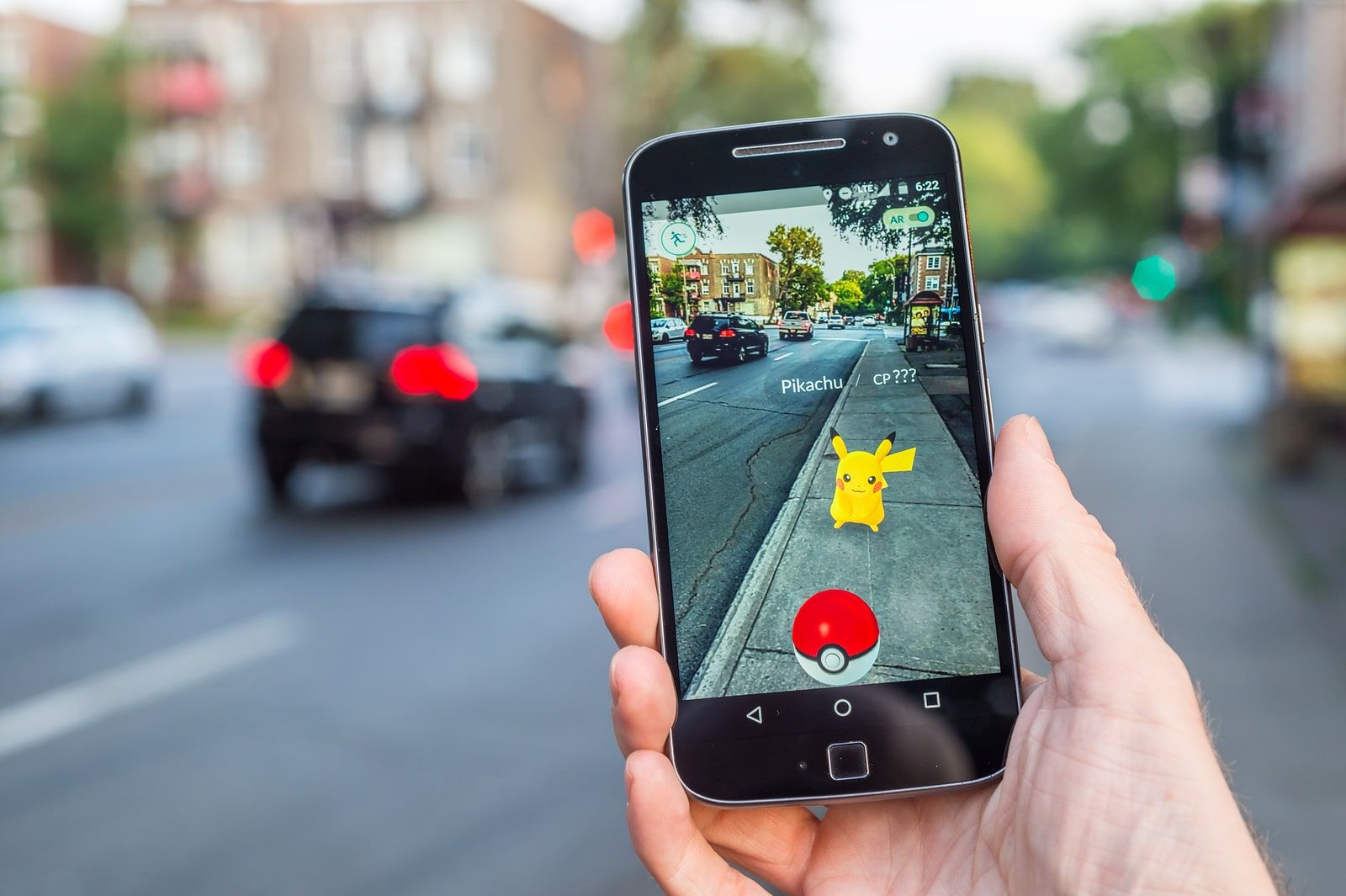
1. AR in Gaming and Entertainment
Augmented reality is a technology that overlays digital information and virtual objects onto the real world. It has gained popularity in gaming and entertainment, with applications like Pokemon Go and Snapchat filters. AR enhances the user experience by merging the virtual and physical worlds, creating immersive and interactive environments. As AR technology continues to advance, we can expect more innovative and engaging experiences in gaming, movies, and live events.
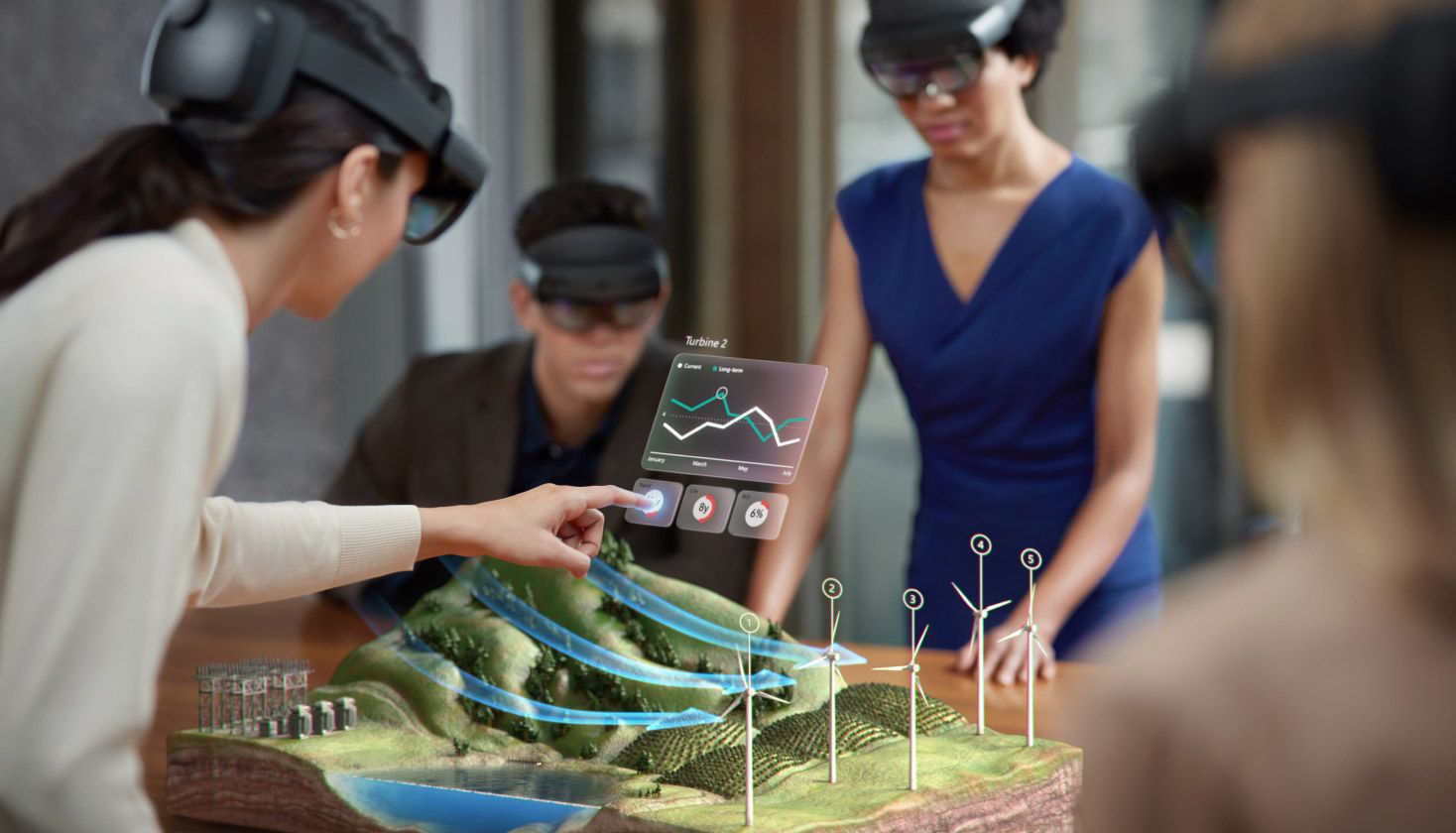


2. AR in Industrial and Medical Fields
Beyond gaming and entertainment, augmented reality holds significant potential in industrial and medical fields. In industrial settings, AR can provide real-time information and guidance to workers, improving efficiency and safety. In the medical field, AR can assist surgeons during complex procedures by overlaying patient information and visualizations onto their field of view. AR has the potential to revolutionize training, maintenance, and visualization processes across various industries.
Blockchain Technology
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Blockchain technology has paved the way for decentralized finance, often referred to as DeFi. DeFi platforms leverage blockchain's transparency and security to enable peer-to-peer financial transactions without the need for intermediaries. This includes activities such as lending, borrowing, and trading digital assets. DeFi has the potential to disrupt traditional financial systems by providing greater accessibility, transparency, and financial inclusion.

2. Supply Chain Management and Transparency
Blockchain technology also offers advantages in supply chain management and transparency. By recording transactions and product information on a shared and immutable ledger, blockchain can enhance traceability, reduce fraud, and improve supply chain efficiency. Consumers can have greater confidence in the authenticity and sustainability of the products they purchase, while companies can streamline their operations and reduce costs.
Additionally,
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Like AI and Machine Learning, Robotic Process Automation, or RPA, is another technology that is automating jobs. RPA is the use of software to automate business processes such as interpreting applications, processing transactions, dealing with data, and even replying to emails. RPA automates repetitive tasks that people used to do.

Although Forrester Research estimates RPA automation will threaten the livelihood of 230 million or more knowledge workers or approximately 9 percent of the global workforce, RPA is also creating new jobs while altering existing jobs. McKinsey finds that less than 5 percent of occupations can be totally automated, but about 60 percent can be partially automated.
Edge Computing
Formerly a new technology trend to watch, cloud computing has become mainstream, with major players AWS (Amazon Web Services), Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform dominating the market. The adoption of cloud computing is still growing, as more and more businesses migrate to a cloud solution.
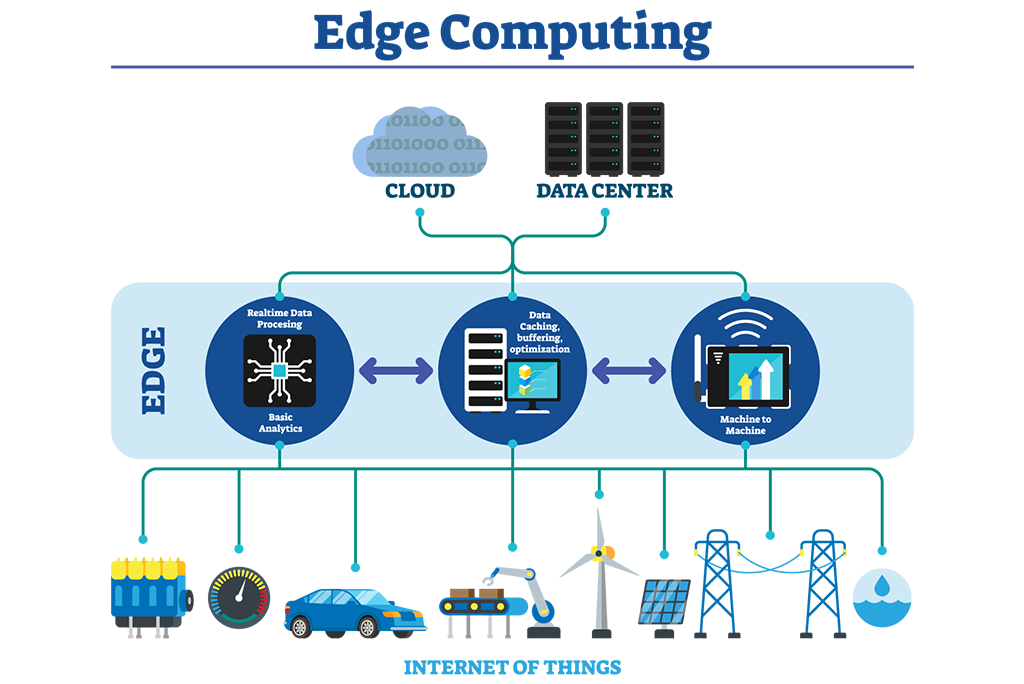
As the quantity of data organizations is dealing with continues to increase, they have realized the shortcomings of cloud computing in some situations. Edge computing is designed to help solve some of those problems as a way to bypass the latency caused by cloud computing and getting data to a data center for processing. It can exist “on the edge,” if you will, closer to where computing needs to happen. For this reason, edge computing can be used to process time-sensitive data in remote locations with limited or no connectivity to a centralized location. In those situations, edge computing can act like mini datacenters.
FAQs
What is the difference between AI, machine learning, and deep learning?
AI refers to the broader concept of creating machines that can perform tasks requiring human intelligence. Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on algorithms and statistical models enabling computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions. Deep learning, a subfield of machine learning, involves training artificial neural networks with multiple layers to automatically learn and extract complex patterns and representations from data.
What are some potential use cases for blockchain beyond cryptocurrencies?
Beyond cryptocurrencies, potential use cases for blockchain include supply chain management, decentralized identity management, smart contracts for automation and transparency, secure and transparent voting systems, and improved data security and privacy in healthcare.
What is the difference between virtual reality and augmented reality?
Virtual reality (VR) refers to a completely immersive digital experience where users are transported to a simulated environment, often through the use of a head-mounted display and motion-tracking technology. Augmented reality (AR), on the other hand, overlays digital information and virtual objects onto the real world, enhancing the user's perception and interaction with their physical surroundings through devices like smartphones or smart glasses.
Conclusion
The latest tech topics discussed in this article highlight the rapid advancements and potential impact of emerging technologies. Artificial intelligence, quantum computing, augmented reality, and blockchain are transforming industries and opening up new possibilities. As these technologies continue to evolve, it is important to stay informed and explore their applications, while also addressing the ethical and societal implications they bring. By embracing these innovations responsibly, we can harness their potential for the betterment of society and the advancement of human progress.






