AI Ethics: Unraveling the Moral Dilemma
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has gained increasing significance in society, emphasizing the imperative for ethical considerations in its creation and implementation.
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has gained increasing significance in society, emphasizing the imperative for ethical considerations in its creation and implementation. AI ethics entails guiding principles that direct the responsible and equitable development and utilization of AI. These principles ensure the responsible use of AI technology, emphasizing safety, security, humanity, and environmental consciousness. Key aspects encompass avoiding bias, safeguarding user privacy and data, and mitigating environmental risks.
The impact of AI on society is substantial, offering the potential to significantly enhance workplace efficiencies and augment human capabilities. Automation of repetitive or hazardous tasks by AI allows human workers to focus on areas where their skills, such as creativity and empathy, are better suited. However, the learning curve of evolving technologies introduces the risk of miscalculations and unintended negative consequences. Consequently, swift recognition and addressing of potential harm in AI systems are paramount.
The responsible development and deployment of AI play a pivotal role in fostering trust and fairness in the application of AI technologies. It ensures that AI systems uphold human values, minimize bias and discrimination, protect privacy, and operate transparently and explainably. The UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights offer substantial value in endeavors to achieve responsible AI development and deployment. Serving as a roadmap, these principles outline key priorities and goals for AI investments, emphasizing the need for states to implement a "smart-mix" of regulation, guidance, incentives, and transparency requirements to advance corporate responsibility and accountability for human rights impacts.
Understanding AI Ethics
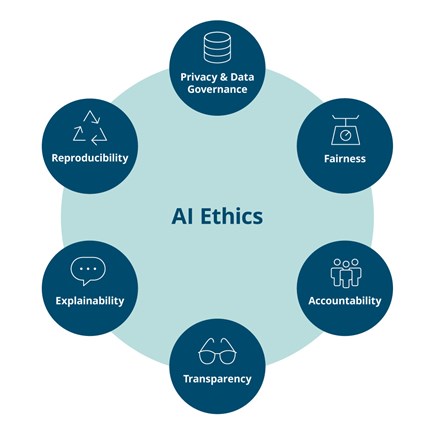
AI ethics stands at the intersection of technology, morality, and societal impact, constituting a multidisciplinary field dedicated to optimizing the beneficial impact of artificial intelligence while mitigating risks and adverse outcomes. At its core, AI ethics revolves around a set of moral principles that act as a compass, guiding the development and deployment of AI systems to ensure alignment with human values, the avoidance of undue harm, and a positive contribution to society.
Transparency:
One foundational principle in ethical AI development is transparency. AI systems are expected to be transparent and explainable, meaning that their decision-making processes should be comprehensible to humans. This transparency not only fosters trust and confidence in AI technology but also serves as a mechanism to reduce the risk of errors and misuse. Moreover, transparency enables both internal and external oversight, providing a means for accountability in the development and deployment of AI systems.
Fairness:
Another pivotal ethical principle is fairness, emphasizing the equal treatment of all individuals or groups by AI systems. Regardless of underlying characteristics such as age, gender, race, or socioeconomic status, ethical AI requires that systems avoid bias and discrimination. Fairness in AI is not only an ethical imperative but also holds economic and social significance. It acts as a crucial safeguard to prevent AI systems from perpetuating or amplifying existing biases within society.
Accountability:
AI systems, like any other technology, should be accountable for their actions. This principle implies that organizations or individuals involved in designing, developing, operating, or deploying AI systems are responsible for ensuring their proper functioning. Accountability in AI is a key factor in reducing the risk of errors and misuse. It also serves to distribute responsibility among stakeholders and allows for both internal and external oversight, ultimately demonstrating respect for individuals impacted by these systems.
Privacy:
Respecting the privacy of individuals emerges as a fundamental principle in AI ethics. AI systems are expected to protect personal data and refrain from using it to manipulate or discriminate against individuals. Privacy protection is indispensable for ensuring the trustworthiness of AI systems. It not only upholds individuals' rights to privacy but also contributes to maintaining the integrity and ethical standards of AI applications.
Unraveling Bias in AI Algorithms and Strategies for Fair Development
Unveiling Amazon's Hiring Tool Bias : Explore the specifics of Amazon's Hiring Tool case, delving into the revelations of systematic discrimination against women in technical job applications. Examine the AI's reliance on a decade's worth of resumes, primarily from male applicants, and how this skewed dataset contributed to a biased system favoring male candidates. This real-world example underscores the potential pitfalls of biased AI in the hiring process.
Facial Recognition Disparities: Investigate the biases present in facial recognition systems, emphasizing their reduced accuracy for people of color and women. Explain how the over-representation of certain demographic groups in training data, such as white individuals, can lead to errors and inaccuracies in recognizing faces from underrepresented communities. Highlight the broader societal implications of biased facial recognition technologies, particularly in areas like surveillance and security.
Scrutinizing the COMPAS Algorithm
Analyze the alleged racial bias in the COMPAS Algorithm, a tool used in the US criminal justice system for predicting recidivism. Discuss how this algorithm's predictions have faced scrutiny for potential discriminatory impacts, shedding light on the challenges and risks associated with biased AI in law enforcement. Explore the consequences of such biases in critical decision-making processes and their implications for fairness and justice.
Real-world Consequences of Bias: Examine the tangible and far-reaching consequences of biased AI in various sectors, including hiring, lending, and law enforcement. Illustrate how unfair treatment resulting from biased algorithms can have profound effects on individuals and communities. Emphasize the erosion of trust among marginalized groups, hindering their participation in economic and societal activities. Discuss the potential costs and repercussions faced by companies neglecting to address AI bias, emphasizing the urgency of mitigating these real-world impacts.
Strategies for Bias Identification and Mitigation: Explore the proposed strategies for identifying and mitigating bias in machine learning models. Discuss the importance of diverse teams in recognizing and addressing bias, and explain pre-processing, in-processing, and post-processing algorithms designed to ensure fairness. Highlight the necessity of regular monitoring and updating of AI models and features to adapt to changes in data distribution. Conclude with the acknowledgment that while these strategies offer valuable tools, continuous efforts are imperative for ensuring fairness in AI systems.
Challenges and Ethical Dilemmas
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into various aspects of our lives has introduced a host of challenges and ethical dilemmas, particularly concerning the collection and utilization of personal data. A notable concern is the lack of transparency in AI decisions, as they often remain inscrutable to human understanding, especially in critical scenarios affecting individuals' lives. Another pressing issue revolves around the inadvertent perpetuation of biases present in the data on which AI systems are trained, potentially resulting in discriminatory outcomes that disproportionately impact specific groups.
Privacy and security challenges have escalated with the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, rendering sensitive information more vulnerable than ever. This has raised questions about how to safeguard private data effectively. Moreover, ethical dilemmas emerge when individual preferences clash with regulatory requirements regarding data usage. For instance, a scenario may arise where the government mandates the release of data that an individual wishes to keep confidential, highlighting the intricate ethical landscape surrounding AI and data privacy.
Addressing these challenges is paramount for fostering responsible and ethical AI deployment in our increasingly data-centric environment. Striking a balance between technological advancements and safeguarding individual rights and privacy necessitates ongoing efforts and a multidisciplinary approach involving technology developers, policymakers, and society at large.
Rules and Frameworks
Data protection laws, a cornerstone in this endeavor, concentrate on enhancing data stewardship, risk management, implications of data use, and mechanisms for transparency and redress. These laws form a regulatory framework to govern AI applications, providing guidelines for responsible data handling and mitigating potential privacy risks. The Privacy by Design approach, delineated in the ISO 31700 Privacy by Design Standard, advocates for embedding privacy considerations into AI systems right from their inception. By promoting a proactive stance toward privacy, organizations can address potential concerns at the outset, fostering responsible AI development.
AI governance has also seen the rise of self-regulatory initiatives within the private sector to deliberate on ethical dimensions of AI development and deployment. Examples include the Partnership on AI to Benefit People and Society, The Montreal Declaration for a Responsible Development of Artificial Intelligence, and The Toronto Declaration. These initiatives contribute to shaping ethical guidelines and best practices, fostering collaboration between stakeholders to ensure AI advancements align with ethical standards and prioritize user privacy.
Impact of AI on Employment
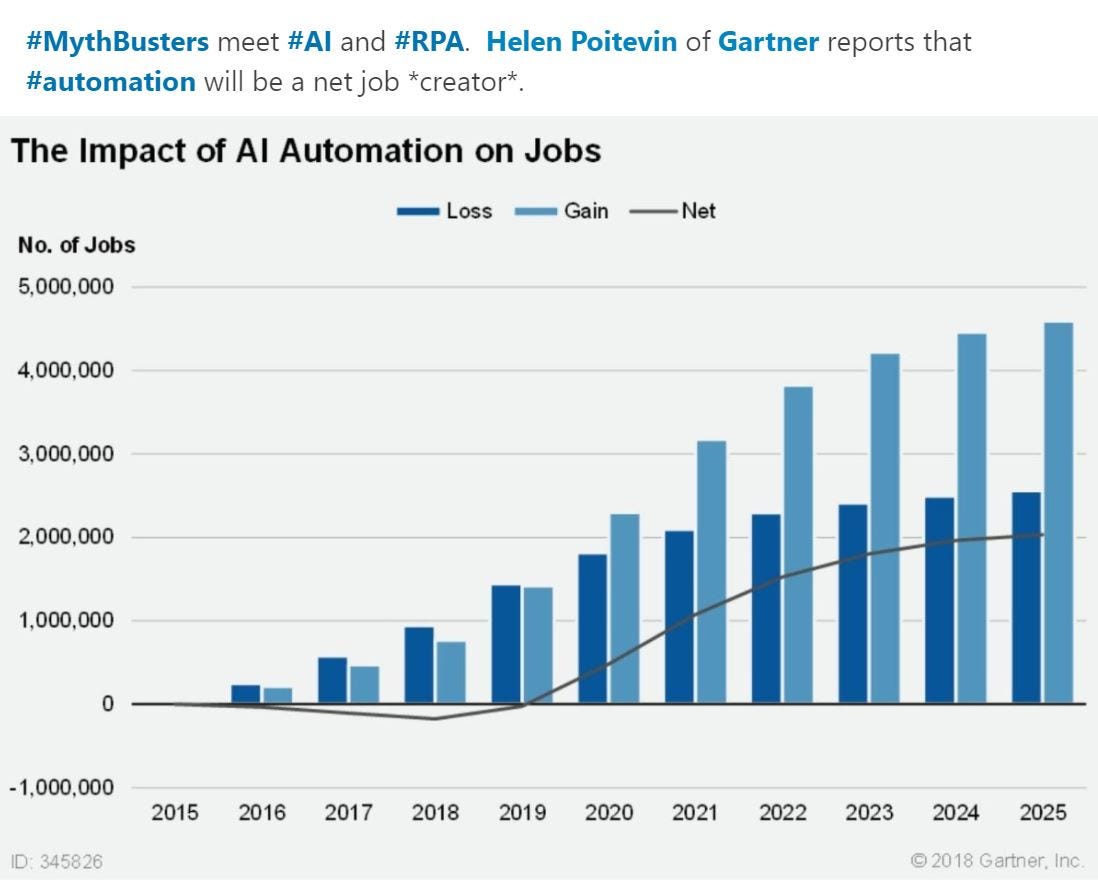
The swift progression of artificial intelligence (AI) has prompted apprehensions regarding its implications for employment and the potential displacement of jobs. Forecasts indicate a transformative impact on the job market, with an estimated 85 million jobs at risk of being replaced by AI and autonomous machines. However, there is a silver lining, as this surge in automation is anticipated to create approximately 97 million new positions by 2025. This dynamic suggests a significant shift in the labor market, emphasizing transformation rather than outright job loss. One of the noteworthy concerns associated with AI's influence on employment is the potential for lower wages, particularly among workers engaged in repetitive and manual tasks. The introduction of AI technologies may lead to wage pressures, requiring a careful examination of the economic implications for the workforce.
Furthermore, AI's advancement has been particularly pronounced in areas such as information ordering, memorization, perceptual speed, and deductive reasoning. While these developments signify progress, they also underscore a growing impact on high-skilled, white-collar jobs. This departure from the historical pattern, where automation primarily affected routine tasks performed by lower-skilled workers, introduces new dimensions to the evolving landscape of employment and skill requirements. As such, adapting to these changes necessitates strategic considerations for workforce development, reskilling initiatives, and thoughtful policy frameworks to address the challenges and opportunities arising from the integration of AI in the workforce.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive exploration of AI ethics has delved into key concerns, including bias, privacy, employment impact, and future challenges. As we navigate the ethical dimensions of AI, it's crucial to remain informed, engage in discussions, and advocate for responsible development. Staying vigilant ensures active participation in shaping ethical standards and safeguards the positive impact of AI on society. Embracing transparency, collective awareness, and responsible advocacy are integral to steering AI towards a future that aligns with ethical principles and benefits humanity.




